[ 딥러닝 ] CNN case study
Updated:
LeNet
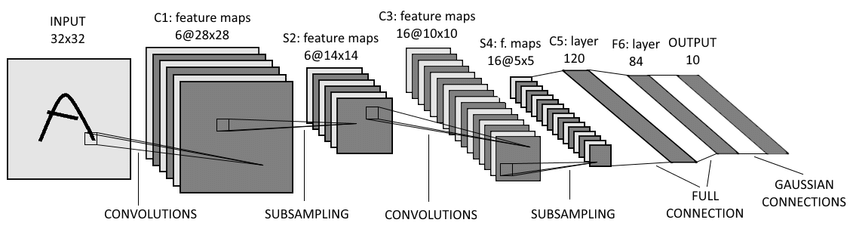
- CNN에서 가장 basic한 모델
Conv Filters
- 5*5 kernel, stride 1
Pooling Layers
- 2*2 kernel, stride 2
Architecture
Conv → Pool → Conv → Pool → Conv → FC → FC
ResNet
- 굉장히 deep한데 (128 layers) 성능이 좋다!
Plain Network의 한계점
- ResNet의 핵심 아이디어인 skip connection이 없는 CNN
- layer가 깊어질수록…
- Gradient Vanishing/Exploding 발생
- parameter를 업데이트하기 위해 gardient descent를 하게 되는데, 이 때 gradient값이 너무 작거나 큰 값들이 계속 곱해지면 결국 vanishig 혹은 exploding하게 된다.
-
layer를 너무 많이 쌓으면 training error가 높게 나타난다.
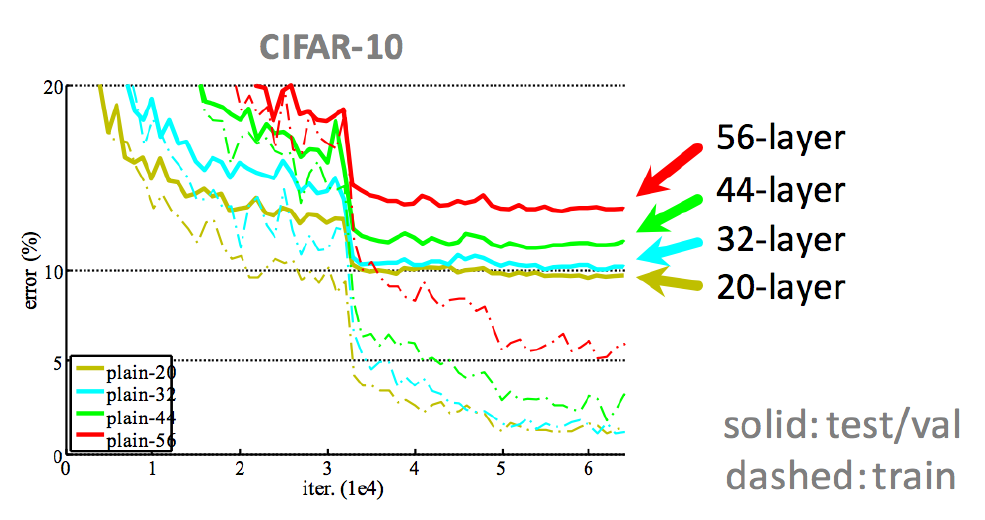
- Gradient Vanishing/Exploding 발생
ResNet의 핵심 아이디어 - Skip (Shortcut) Connection
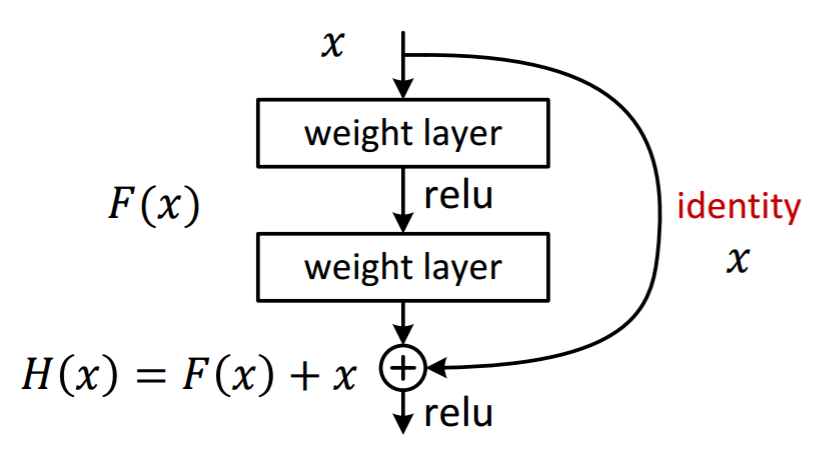
- 입력 $x$를 몇 layer 이후의 output에 더해준다.
- output에서의 gradient를 구하면 $\frac{\partial H}{\partial x}=\frac{\partial F}{\partial x}+1$ 이 되므로 $\frac{\partial H}{\partial x}$이 0이 되지 않아 Gradient Vanishing/Exploding 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
Architecture
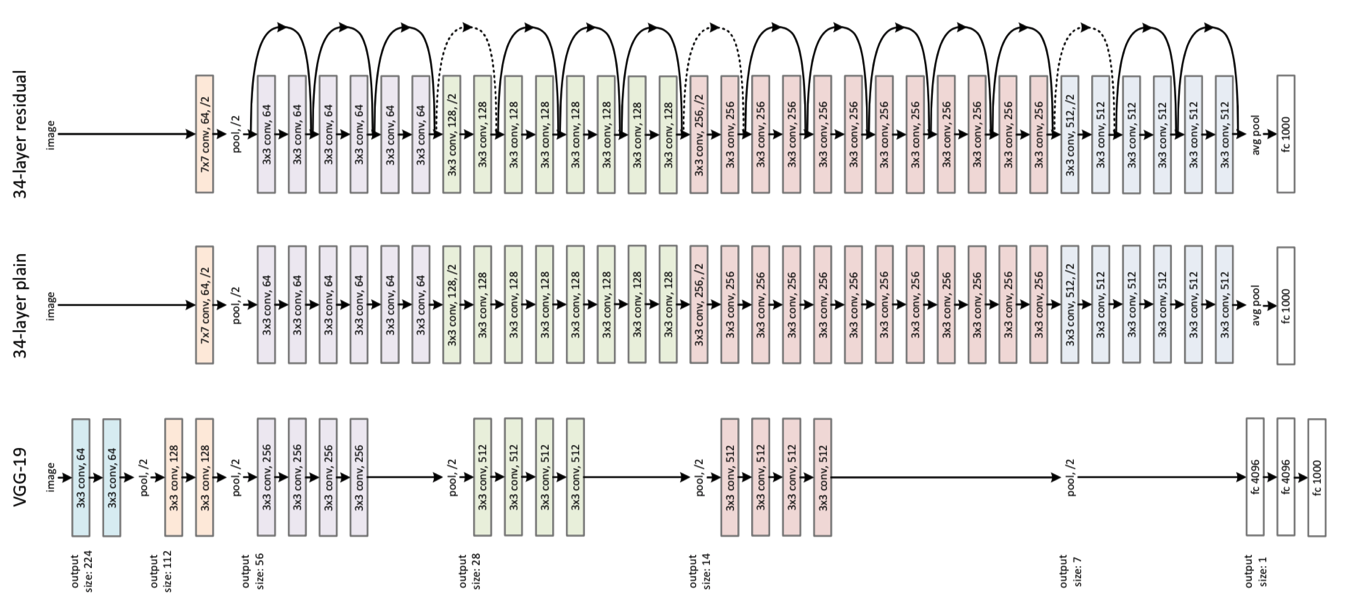
- 위에서부터 순서대로 residual net, plain net, VGG-19
- ResNet은 VGGnet 구조에서 가져온 것이다.
-
skip connection의 조건 : $x$의 size = output의 size
\[H(x)=F(x,\{W_i\})+x,\,\,\, F(x,{W_i})=W_2\sigma(W_1x)\]-
만약 size가 동일하지 않다면 linear projection $W_s$를 적용할 수 있다.
\[H(x)=F(x,\{W_i\})+W_s x\]
-
- input size < output size일 때 사용하는 3가지의 skip connection
- 증가하는 차원에 대해 추가적으로 zero padding을 적용하여 identity mapping 수행
- 차원이 증가할 때만 projection shortcut을 사용합니다.
- 모든 shortcut이 projection입니다.
